Aesthetics
Face
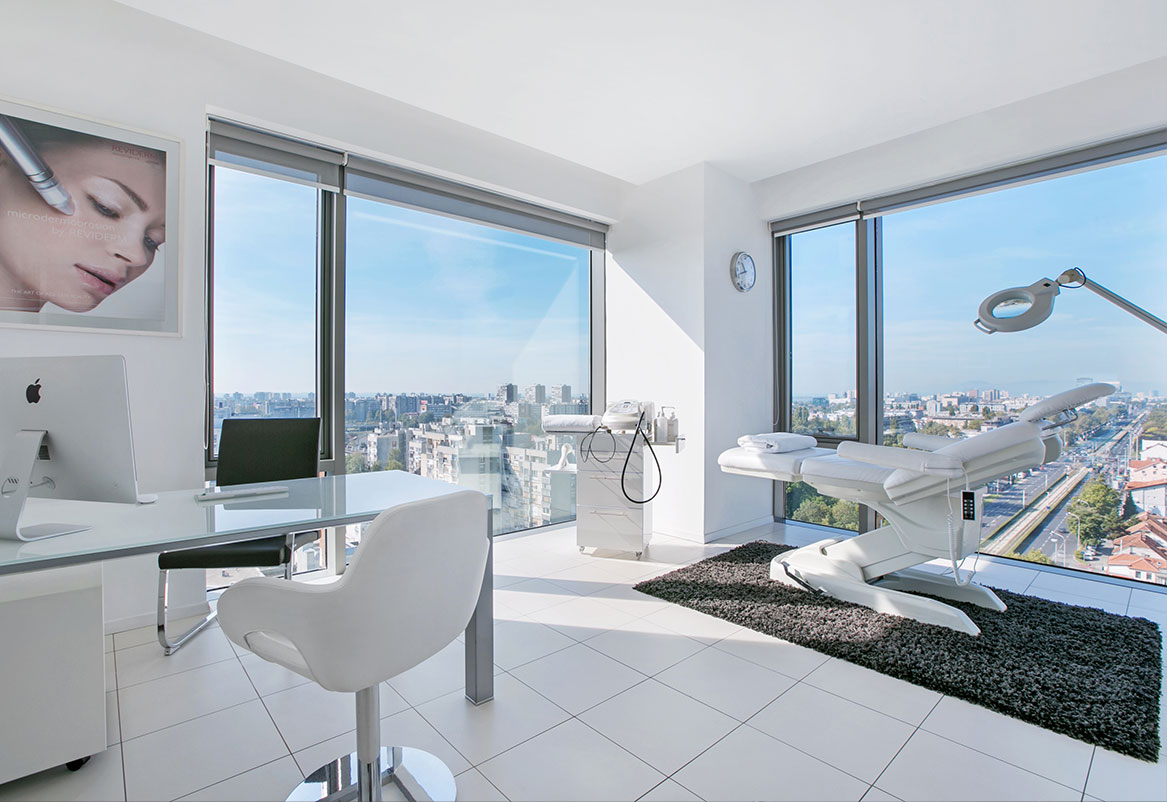
The most modern facial treatments help you look younger, more elegant and happier.
Body
Feel comfortable in your body and correct sources of discomfort.
Chest
Make your wish for a better appearance come true and restore your self-confidence with aesthetic correction.
Hair and scalp
Minimally invasive solutions for hair loss and a natural look.
Issues
Find solutions to some of the most common aesthetic problems.
Treatments
Surgery
Treatments

Hair and scalp mesotherapy
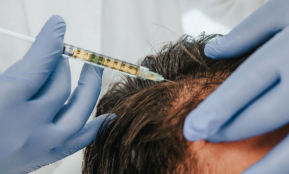
Thinning hair therapy with your own blood

Trichotest – DNA analysis of hair loss and baldness

Hair loss in women – causes and how to prevent it

Hair loss in men – causes and how to prevent it
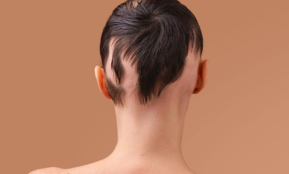
Alopecia – hair loss
FACE

BODY
Implantology Center
Different methods of solving the problem of missing one or more teeth.
Prosthetics
The most common solution in cases of functional or aesthetic tooth damage.
Aesthetic Dentistry
Harmonious tooth shaping and tooth color correction according to your wishes.
General Dentistry
Modern and timely diagnostics, treatment and dental hygiene are the key to the health of your teeth.
Issues
Find solutions to some of the most common aesthetic problems.
About us
Locations
Causes of dry skin
The causes of dry skin can be varied and are often the result of a combination of internal and external factors. Here are some of the main causes:
-
Climatic conditions
Winter conditions with low temperatures and low humidity can cause skin to dry out. Climates with low humidity, including arid areas, can also dry out skin.
-
Hot showers and baths.
Prolonged exposure to hot water can remove natural oils from the skin, leading to dryness.
-
Aging
With age, the skin loses its ability to retain moisture and produces less sebum, which can lead to dryness.
-
Health conditions
Health conditions such as eczema, psoriasis, diabetes, and hypothyroidism can affect skin dryness.
-
Sun exposure
UV rays can damage the skin and reduce its ability to retain moisture.
-
Dehydration
Insufficient fluid intake can reduce skin moisture.
The influence of the environment on skin dryness
The environment plays a significant role in the condition of our skin, including its moisture content and tendency to dryness.
Here’s how different environmental factors can affect skin dryness:
-
Climatic conditions
Winter conditions with low temperatures and low humidity can cause dry skin. Wind can further damage the skin and remove protective oils, making the skin dry and chapped.
Climates with high temperatures and low humidity, such as desert areas, can also cause skin to dry out. Sweating in hot conditions can lead to moisture loss, and dry air can further aggravate the condition. -
UV radiation
Long-term exposure to UV rays can damage the skin barrier, reduce its ability to retain moisture, and accelerate skin aging, which can cause dryness and rough texture.
-
Air pollution
Toxins and pollutants in the air, such as smoke, dust, and chemicals, can damage the skin's protective barrier, causing inflammation and dryness. They can also increase oxidative stress on the skin, which contributes to aging and dryness.
-
Wind
Exposure to wind can remove natural oils from the skin's surface, which can lead to dryness, chapping, and irritation.
-
Water
Water containing high levels of minerals, such as calcium and magnesium, can leave deposits on the skin, which can interfere with natural hydration and lead to dryness. The chlorine in pool water can dry out the skin and damage the skin's protective barrier.
Dry skin and nutrition
Nutrition has a significant impact on skin health, including its hydration and elasticity. A balanced diet rich in nutrients can help keep skin healthy and prevent dryness.
Omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids help maintain a healthy skin barrier and prevent moisture loss. Foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids include fatty fish (salmon, mackerel, sardines), flaxseed, chia seeds, and walnuts. Omega-6 fatty acids are found in vegetable oils (sunflower, corn oil).
Numerous vitamins such as vitamins E, A, C, and D can affect skin hydration and moisture.
Vitamin E is an antioxidant that helps protect the skin from free radical damage and keeps it hydrated. It is found in nuts, seeds, avocados, and vegetable oils.
Vitamin A helps in renewing the skin and maintaining its elasticity. It is found in carrots, sweet potatoes, spinach, kale and liver.
Vitamin C helps in the production of collagen and protects the skin from oxidative stress. It is found in citrus fruits, strawberries, peppers, broccoli and kiwi.
Vitamin D helps maintain healthy skin, and a deficiency can lead to dryness. It is found in fatty fish, eggs, and dairy products, and is also synthesized in the skin through exposure to sunlight.
In addition to fatty acids and vitamins, minerals such as zinc and selenium help restore skin and maintain skin elasticity.
We must not forget about skin hydration. Drinking enough fluids is key to keeping your skin hydrated. It is recommended to drink at least 8 glasses of water a day, and fluid intake can be increased by consuming fruits and vegetables with a high water content, such as watermelon, cucumbers, and oranges.
Tips for dry skin care
-
Moisturizing creams
Use moisturizers that contain ingredients such as glycerol, hyaluronic acid, urea, ceramides, and lanolin. It's best to apply moisturizer right after showering while your skin is still damp.
-
Avoid hot showers and baths
Use lukewarm water instead of hot, as hot water can strip the natural oils from the skin. Also, choose products without fragrance and aggressive chemicals. Mild soaps and syndets (synthetic detergents) are better for dry skin.
-
Maintaining hydration
It is recommended to drink at least 8 glasses of water a day. Include foods rich in essential fatty acids, vitamins and antioxidants in your diet, such as nuts, seeds, fruits and vegetables.
-
Daily routine
For facial care, use mild facial cleansers, apply a serum with hyaluronic acid, and use a rich night cream that will provide additional hydration during the night.
-
Going to the dermatologist
If you have chronically dry skin or a condition that doesn't respond to home treatments, a consultation with a dermatologist may be helpful. They may recommend medical treatments or special products.
How dry skin affects older adults
Dry skin can significantly affect older adults due to the natural changes in the skin that come with age.
As we age, the skin’s production of sebum (natural oils) decreases, which reduces the skin’s natural hydration. The skin becomes thinner and less elastic, making it more susceptible to dryness and damage.
As we age, our skin’s ability to retain moisture decreases, resulting in dryness. Also, reduced blood circulation can reduce the skin’s supply of nutrients and moisture.
BLOG SUGGESTION
























