Aesthetics
Face
The most modern facial treatments help you look younger, more elegant and happier.
Body
Feel comfortable in your body and correct sources of discomfort.
Chest
Make your wish for a better appearance come true and restore your self-confidence with aesthetic correction.
Hair and scalp
Minimally invasive solutions for hair loss and a natural look.
Issues
Find solutions to some of the most common aesthetic problems.
Treatments
Surgery
Treatments

Hair and scalp mesotherapy
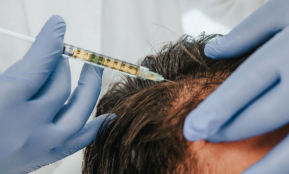
Thinning hair therapy with your own blood

Trichotest – DNA analysis of hair loss and baldness

Hair loss in women – causes and how to prevent it

Hair loss in men – causes and how to prevent it
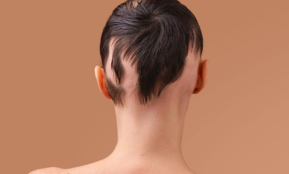
Alopecia – hair loss
FACE

BODY
Implantology Center
Different methods of solving the problem of missing one or more teeth.
Prosthetics
The most common solution in cases of functional or aesthetic tooth damage.
Aesthetic Dentistry
Harmonious tooth shaping and tooth color correction according to your wishes.
General Dentistry
Modern and timely diagnostics, treatment and dental hygiene are the key to the health of your teeth.
Issues
Find solutions to some of the most common aesthetic problems.
About us
Locations
How missing multiple teeth affects functionality and aesthetics
-
Functionality
Difficulty chewing: When multiple teeth are missing, chewing becomes difficult or even impossible in some parts of the mouth. This can lead to poorer food digestion and absorption of nutrients.
Improper bite: Losing teeth can change the way your jaws close, which can lead to bite problems. This can put extra strain on your remaining teeth and even cause pain in your temporomandibular joint (TMJ) or facial muscles.
Movement of remaining teeth: When teeth are missing, the remaining teeth tend to move towards the empty spaces, which can lead to an uneven bite and make it difficult to maintain oral hygiene.
-
Aesthetics
Changes in facial appearance: Missing multiple teeth can lead to a loss of support for the lips and cheeks, which can result in a sunken or sunken appearance. This can give the impression of an older appearance, even in younger people.
Reduced self-confidence: Missing teeth can affect the way a person smiles or speaks, which can lead to decreased self-confidence and social awkwardness.
Aesthetic irregularities in the smile: Missing teeth cause gaps and unevenness in the smile, which can negatively affect the overall aesthetics of the face.
Different options for replacing multiple teeth
-
Dental implants
Dental implants are artificial replacements that are implanted into the jawbone to replace the roots of missing teeth.
A screw-shaped implant is placed in the jawbone where the tooth is missing, and an implant suprastructure is placed on top of it, on which the prosthetic work is then placed. -
Dental bridge
A dental bridge is a type of permanent prosthetic work used to replace one or more missing teeth. A bridge consists of two or more interconnected crowns that are fixedly attached to natural teeth or implants on either side of the gap.
-
Dental crowns
Ceramic crowns, also known as porcelain crowns, porcelain teeth, porcelain veneers, are the most common prosthetic solution in cases of functional or aesthetic tooth damage.
They are made of ceramic that perfectly imitates the color of the tooth, and the crown itself protects the tooth from further damage and prevents its further decay.
Advantages and disadvantages of fixed and mobile prosthetic solutions
-
Fixed prosthetic solutions (bridges and implants):
Advantages
Fixed solutions such as implants and bridges are very stable, providing a feeling similar to natural teeth. Fixed prosthetic restorations look more natural and are more aesthetically appealing because they are made to fit perfectly into the natural dental arch. With proper care, fixed prosthetic solutions can last for many years, often more than a decade.
Disadvantages
Fixed solutions, especially implants, can be significantly more expensive than removable prostheses. The placement of fixed prosthetic solutions often requires a more complex and lengthy procedure, including surgical procedures, especially with implants. Fixed solutions require a certain amount of healthy dental tissue or bone, which is not always the case for all patients. -
Mobile prosthetic solutions (dentures):
Advantages
Removable dentures are usually more affordable than fixed dentures, making them more accessible to a wider range of patients. The process of making and fitting removable dentures is usually faster, so patients can receive their replacement in less time. Removable dentures can be more easily adjusted in the event of changes in the dental arch or jaw.
Disadvantages
Removable dentures are not as stable as fixed solutions, so they can move or fall out during chewing or speaking, which can cause discomfort. Chewing can be difficult because removable dentures do not provide the same strength and effectiveness as fixed solutions. Although removable dentures can now be made to look more natural, they are not always as aesthetically pleasing as fixed options. Removable dentures need to be removed and cleaned regularly, and may require adjustments over time as your mouth changes.
The process of making prosthetic work
-
First examination and consultation
The dentist first assesses the condition of the patient's teeth, gums, and jaw to determine what type of prosthetic work is most appropriate. He or she may use X-rays, digital scans, and models to get the complete picture.
-
Preparation of the tooth cavity
In the case of fixed prosthetic solutions such as crowns or bridges, the teeth are shaped (ground) to allow the prosthetic work to be placed. If implants are placed, a surgical procedure is performed to place the implants in the jawbone. The dentist takes precise impressions of the teeth and jaw using special materials or digital scanners. These impressions are used to create an accurate model of the future prosthetic work.
-
Laboratory phase
The impressions or digital scans are sent to a dental laboratory where technicians create a plaster or digital model of the teeth. Based on the model, technicians create crowns, bridges, implants, dentures, or other prosthetic replacements. Depending on the type of material (ceramic, metal, acrylic), the process may include casting, ceramic layering, polishing, and other techniques.
-
Prosthetic work trial
The dentist checks how the prosthetic work fits the patient's teeth and jaw. This stage allows for adjustments to the color, shape, and size of the prosthetic work. If corrections are needed, the prosthetic work is returned to the laboratory for finishing.
-
Final installation
When the prosthetic work is ready, the dentist permanently cements or fixes it to the teeth or implants.
The dentist checks the bite and makes adjustments if necessary to ensure comfort and functionality. -
Control and maintenance
After final installation, the patient should come for regular check-ups so that the dentist can monitor the condition of the prosthetic work.
The patient is counseled on proper oral hygiene and care for the prosthetic work to ensure its longevity.
Care and maintenance of prosthetic work
-
Oral hygiene
Brush your teeth and dentures at least twice a day with a soft toothbrush. Use a low-abrasive toothpaste to avoid damaging the denture surface.
Use dental floss, interdental brushes, or a water irrigator (waterpik) to thoroughly clean the areas between your dentures and your natural teeth or implants. This is especially important with bridges and implants, where bacteria and plaque can build up under and around the dentures. -
Regular visits to the dentist
Visit your dentist at least twice a year for regular checkups and professional cleanings. Your dentist will check the condition of your dentures and gums, and make any necessary adjustments or repairs.
If you notice any discomfort, shifting, cracks, or damage to your prosthetic work, contact your dentist immediately. -
Proper nutrition
Hard nuts, candy, or ice can damage or loosen your dentures. Try to avoid them to extend the life of your dentures.
Foods that are sticky, like caramel, can get stuck under dentures or bridges, which can lead to cavities and gum problems. -
Care of removable dentures
Removable dentures should be cleaned after each meal to remove food debris and plaque. Use a special toothbrush and denture cleaner. Do not use regular toothpaste as it may be too abrasive.
Before going to bed, remove the prosthesis and soak it in a solution for cleaning the prosthesis or plain water. This helps preserve the shape of the prosthesis and prevents the material from drying out. -
Care of fixed prosthetics (bridges, crowns, implants)
Although implants are not susceptible to decay, the gums and surrounding tissue can be susceptible to infection. Clean the area around the implants regularly to prevent peri-implantitis (inflammation of the tissue around the implant).
It is recommended to use antiseptic mouthwashes to further reduce the risk of bacterial infections.
TREATMENTS
List of services that can solve the problem of *I am missing several teeth*
BLOG SUGGESTION



















