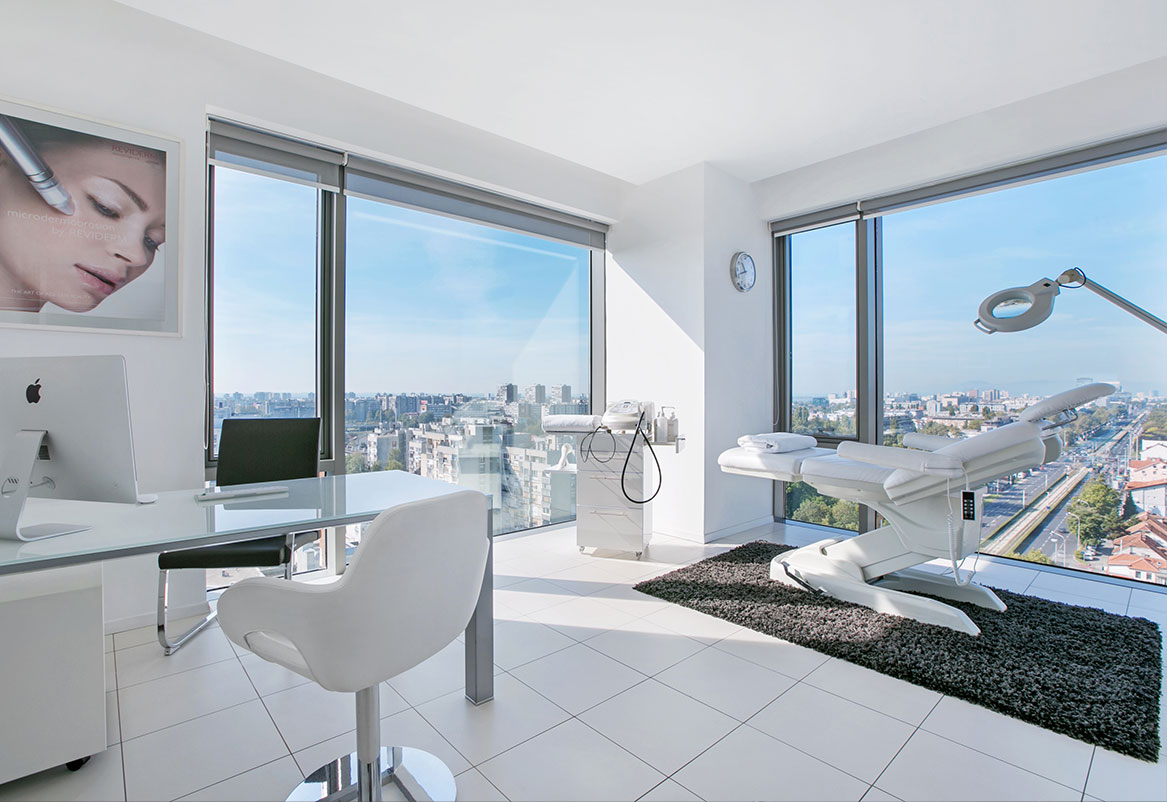
Aesthetics
Face
The most modern facial treatments help you look younger, more elegant and happier.
Body
Feel comfortable in your body and correct sources of discomfort.
Chest
Make your wish for a better appearance come true and restore your self-confidence with aesthetic correction.
Hair and scalp
Minimally invasive solutions for hair loss and a natural look.
Issues
Find solutions to some of the most common aesthetic problems.
Treatments
Surgery
Treatments

Hair and scalp mesotherapy
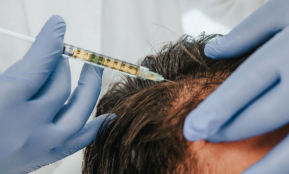
Thinning hair therapy with your own blood

Trichotest – DNA analysis of hair loss and baldness

Hair loss in women – causes and how to prevent it

Hair loss in men – causes and how to prevent it
Alopecia – hair loss
FACE

BODY
Implantology Center
Different methods of solving the problem of missing one or more teeth.
Prosthetics
The most common solution in cases of functional or aesthetic tooth damage.
Aesthetic Dentistry
Harmonious tooth shaping and tooth color correction according to your wishes.
General Dentistry
Modern and timely diagnostics, treatment and dental hygiene are the key to the health of your teeth.
Issues
Find solutions to some of the most common aesthetic problems.
About us
Locations
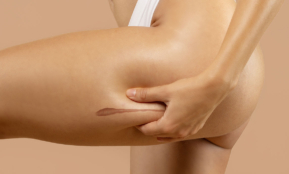
Causes of belly fat
-
Genetics
Genetic factors can influence where your body stores fat. If your family has a tendency to store fat in certain areas, you're likely to have a similar pattern.
-
Hormones
Hormonal changes, such as those that occur during pregnancy, menopause, or stressful situations (increased cortisol levels), can significantly affect fat distribution.
-
Nutrition
High intake of processed foods, sugar, alcohol and saturated fats can contribute to fat accumulation, especially in the abdominal area.
-
Physical activity
Lack of physical activity can contribute to greater fat accumulation, while regular exercise helps burn calories and reduce accumulated fat.
Two main types of fat
-
Subcutaneous fat
Subcutaneous fat is the fatty tissue that lies just beneath the skin. It is the type of fat that is most visible and usually accumulates around the waist, hips, thighs, and lower abdomen.
Although subcutaneous fat can be aesthetically unsightly, it is not associated with as many health risks as visceral fat. However, excessive accumulation of subcutaneous fat can increase the risk of metabolic problems, such as high cholesterol and insulin resistance.
-
Visceral fat
Visceral fat is a type of fat found deep inside the abdomen, surrounding internal organs, such as the liver, heart, and intestines. This type of fat is not visible from the outside, but it has a major impact on health.
Visceral fat is associated with a higher risk of serious health problems, such as heart disease, type 2 diabetes, high blood pressure, and other metabolic disorders. This fat can cause inflammation in the body, which increases the risk of various diseases.
How to reduce belly fat?
-
Reduce your intake of processed foods.
Foods high in sugars, trans fats, saturated fats and refined carbohydrates (such as fast food, sweets, sodas and white bread) can contribute to fat accumulation, especially in the abdominal area.
-
Increase your fiber intake
Fiber helps with digestion and keeps you feeling full. Vegetables, fruits, whole grains, and legumes are excellent sources of fiber.
-
Eat smaller portions, but more often
Smaller, more frequent meals throughout the day help maintain blood sugar balance and prevent overeating.
-
Reduce your alcohol intake.
Alcohol is high in calories, and excessive consumption can contribute to fat accumulation, especially in the abdominal area. A "beer belly" is often a result of excessive alcohol consumption.
-
Drink enough water.
Water helps with hydration, reduces bloating and can help control appetite.
-
Physical activity
Running, cycling, brisk walking, swimming and other cardio exercises can burn calories and reduce overall body fat, including belly fat. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate or 75 minutes of vigorous aerobic activity per week.
Strength training (with weights, body weight or machines) will help build muscle and speed up metabolism. Muscles burn more calories, even at rest, so increasing muscle mass can help burn fat.
Exercises that target the abdominal muscles (like planks, crunches, leg raises) can help tone your stomach, but keep in mind that exercises targeting the abdomen alone will not eliminate fat in that area, but rather burning calories through overall physical activity is important.
-
Stress reduction
High levels of stress can increase the production of the hormone cortisol, which is linked to the accumulation of visceral fat (around internal organs). Relaxation techniques such as meditation, yoga, deep breathing, walks in nature, or any activity that relaxes you can help reduce stress.
-
Gradual weight loss
Extreme diets and rapid weight loss can lead to muscle loss, a slowed metabolism, and even weight regain. It's better to choose moderate, long-term changes in your eating habits that you can maintain.




















