Aesthetics
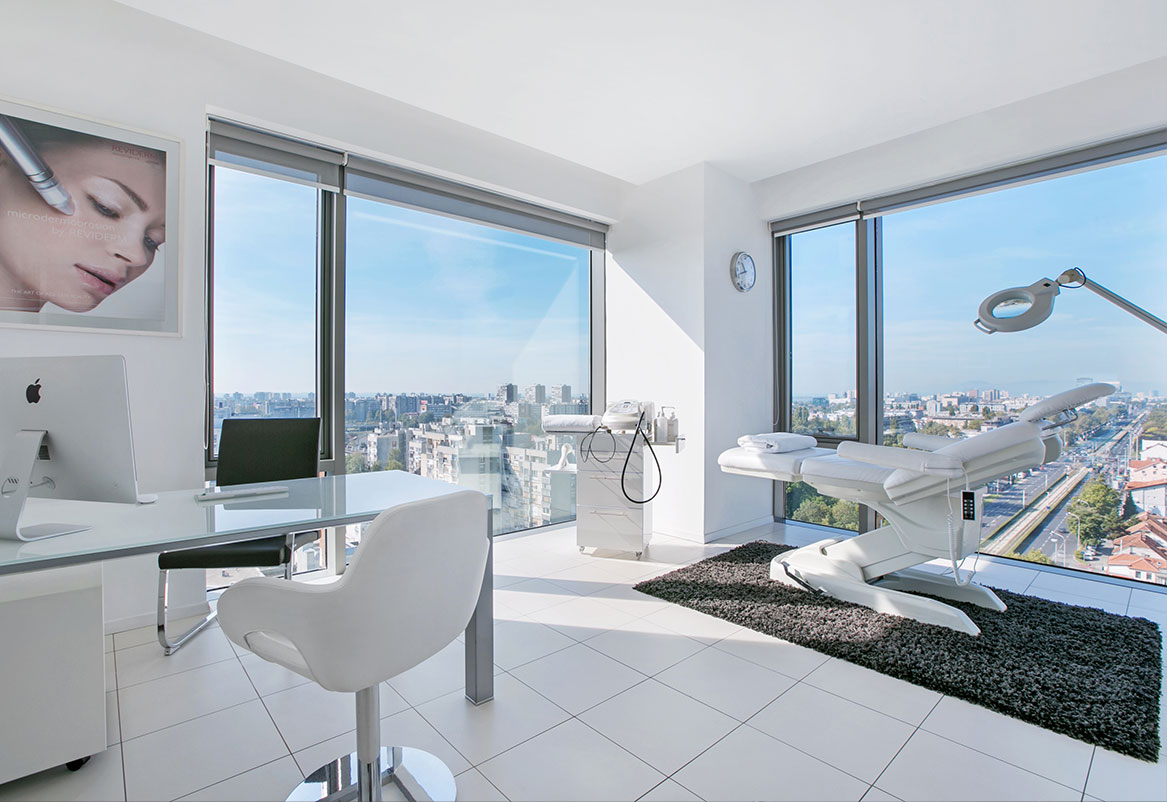
Face
The most modern facial treatments help you look younger, more elegant and happier.
Body
Feel comfortable in your body and correct sources of discomfort.
Chest
Make your wish for a better appearance come true and restore your self-confidence with aesthetic correction.
Hair and scalp
Minimally invasive solutions for hair loss and a natural look.
Issues
Find solutions to some of the most common aesthetic problems.
Treatments
Treatments
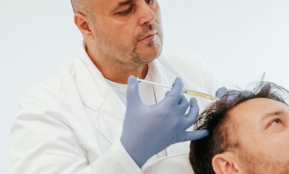
Hair and scalp mesotherapy
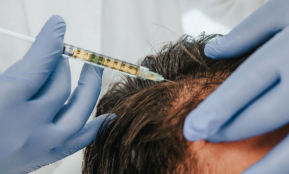
Thinning hair therapy with your own blood

Trichotest – DNA analysis of hair loss and baldness

Hair loss in women – causes and how to prevent it

Hair loss in men – causes and how to prevent it
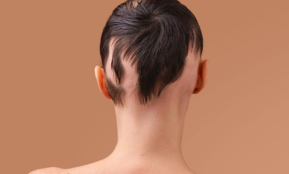
Alopecia – hair loss
FACE

BODY
Implantology Center
Different methods of solving the problem of missing one or more teeth.
Prosthetics
The most common solution in cases of functional or aesthetic tooth damage.
Aesthetic Dentistry
Harmonious tooth shaping and tooth color correction according to your wishes.
General Dentistry
Modern and timely diagnostics, treatment and dental hygiene are the key to the health of your teeth.
Issues
Find solutions to some of the most common aesthetic problems.
About us
Locations
Different types of oral surgery
-
Wisdom tooth extraction
Wisdom teeth often do not have enough space to erupt properly, which can cause pain, inflammation, or damage to neighboring teeth. Surgical extraction may be necessary if the wisdom teeth are partially or completely impacted.
-
Treatment of infections and abscesses
Tooth or gum infections that cannot be resolved with antibiotics sometimes require surgery to remove the abscess or infected tissue.
-
Installation of dental implants
If you are missing one or more teeth, dental implants may be an option. During the procedure, an implant (screw) is placed in the jawbone, and after healing, a crown is placed on top of it to replace the natural tooth.
-
Sinus lift
This procedure is often necessary before placing an implant in the upper jaw if there is not enough bone. During the procedure, the sinus lining is lifted and artificial bone is added to create a sufficient base for the implant.
-
Periodontal surgery
If you have advanced gum disease (periodontitis), periodontal surgery may be necessary to remove infected tissue, clean out deeper pockets around your teeth, or graft tissue to restore receding gums.
-
Jaw correction (orthognathic surgery)
In the case of jaw irregularities that affect bite, speech, or appearance, orthognathic surgery can help correct the position of the jaw.
Preparation for surgery
-
Arrange a consultation with a dentist or oral surgeon
Before the procedure, your dentist or oral surgeon will perform an examination, make a diagnosis, and explain the details of the procedure. Ask questions to understand what to expect and what potential complications are.
-
Report your health status
Tell your surgeon about all the medications you take, including vitamins and herbal supplements. Also, inform them about any health problems, such as allergies, high blood pressure, diabetes, or heart problems.
-
Avoid smoking and alcohol.
For a few days before and after the procedure, avoid smoking and alcohol consumption as they can interfere with the healing process.
Surgical procedure
-
Patient preparation
Before the procedure begins, anesthesia will be administered. This can be local anesthesia (which numbs only the area being treated) or general anesthesia (if the procedure is more complex and requires you to be unconscious).
-
Performing a surgical procedure
Depending on the type of procedure, the surgeon will make incisions to access the tooth, bone, or soft tissues. For example, when removing an impacted wisdom tooth, a small incision may be made in the gum to access the tooth.
Depending on the purpose of the procedure, the surgeon will perform the necessary procedures – this may include removing a damaged tooth, cyst or tumor, placing implants, correcting the jaw, or transplanting tissue.
After the procedure is complete, the area is closed with stitches. Some stitches are self-dissolving, while others will need to be removed after a few days.
-
Final phase and recovery
The surgeon will place sterile gauze over the area to control bleeding. You will be told to gently bite the gauze for about 30-60 minutes.
After the procedure, you will be monitored for some time to ensure you are feeling well, especially if you were under general anesthesia.
Before you leave, you will receive detailed instructions on caring for the procedure area, including information on diet, pain medication, avoiding physical activities, and possible complications.
Care after surgery
-
Pain and swelling
If you are taking painkillers recommended by your doctor, follow the dosage. The most commonly recommended are ibuprofen or paracetamol.
To reduce swelling, apply a cold compress (an ice pack wrapped in a cloth) to the outside of your cheek at 10-15 minute intervals for the first 24 hours.
Swelling is usually most pronounced within 48 hours after the procedure, but should gradually decrease thereafter. -
Nutrition and hydration
Drink plenty of fluids, but avoid alcohol, carbonated drinks, and hot beverages for at least 24 hours after the procedure.
Eat soft, mushy foods such as soups, purees, yogurt, porridge or pudding. Avoid hard, spicy or acidic foods as they can irritate the surgical area.
Do not use a straw while drinking because sucking can dislodge a blood clot and cause complications such as dry socket. -
Oral hygiene
Do not rinse your mouth or brush your teeth for the first 24 hours after the procedure. After that, gently brush your teeth, avoiding the surgical area.
After 24 hours, you can start gently rinsing your mouth with lukewarm salt water (half a teaspoon of salt in a glass of warm water) 3-4 times a day, especially after meals. -
Avoid strenuous activities
Limit physical activity and avoid exercising for at least 2-3 days after the procedure, as exertion can increase the risk of bleeding and swelling.
-
Control examination
Arrange a follow-up appointment as directed by your dentist to check the healing process and remove stitches if necessary.
Possible complications and recovery
-
Infection
Infection can occur if bacteria enter the surgical area. Symptoms include swelling, redness, warmth, bad breath, or pus.
If you suspect an infection, see your dentist immediately as you may need antibiotics. -
Dry socket
Dry socket occurs when a blood clot fails to form or moves too soon from the tooth extraction site, leaving the bone and nerves exposed. This can cause severe pain for several days after the procedure.
This complication is more common after wisdom teeth removal, and symptoms include severe, throbbing pain that spreads to the ear, eyes, or neck. If you notice these symptoms, see your dentist for treatment.
-
Bleeding
Light bleeding is normal for the first 24 hours after the procedure. However, if the bleeding does not stop or becomes heavy, seek medical attention.
To prevent bleeding, avoid physical activity, alcohol, smoking, and using a straw. -
Swelling and bruising
Swelling and bruising are common after surgery and may last for several days. The swelling usually peaks 48 hours after the procedure and then begins to subside.
Applying cold compresses for the first 24 hours can help reduce swelling. After that, warm compresses can help speed up the absorption of swelling and bruising. -
Numbness
Sometimes, temporary numbness of the lips, tongue, or chin may occur due to local anesthesia or nerve irritation during the procedure. This numbness usually disappears after a few hours or days.
If you experience prolonged numbness that lasts more than a few days, contact your dentist. -
Recovery
Follow all instructions from your dentist regarding care of the surgical area, including medication, diet, and oral hygiene.
Drink plenty of water and eat soft, nutritious foods for the first few days. As your recovery progresses, gradually return to your normal diet.
Avoid intense physical activity for the first few days as it may cause bleeding or prolong swelling.
Avoid smoking and alcohol for at least 72 hours after the procedure as they slow down the healing process and increase the risk of complications.
Regular check-ups allow the dentist to monitor the healing process and take necessary steps if complications arise.
TREATMENTS
List of services that can solve the problem of *oral surgery*
BLOG SUGGESTION



















